The sphenoid is located in the middle part of the skull base, between the frontal and ethmoid ahead, behind the occiput.

It has a body and three pairs of processes.
BODY SPHENOID
Cube shape has six sides.
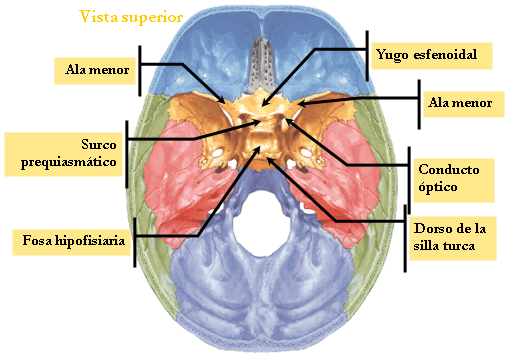
TOP FACE
It is part of the middle floor of the skull base presents:
☻ The jugum the ethmoid sphenoid extension or limiting prosessus forward and backward by the esfenoidalis limbus.
☻ The optical channel containing the optic chiasm and ends outside in optical holes.
The pituitary fossa or sella which houses the pituitary gland limited:
☻ By forward by the pituitary tubercle.
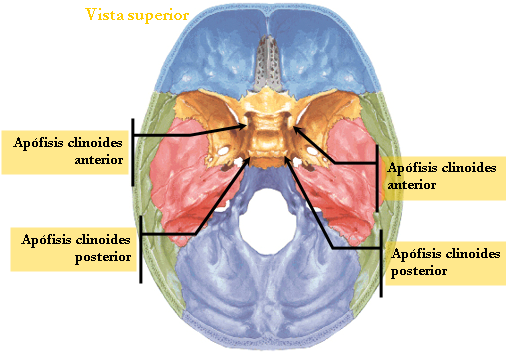
☻ Behind the quadrilateral sheet having laterally to the rear clinoid process.
FORMER FACE
presents:
☻ The ethmoid process that articulates with the horizontal lamina of the ethmoid.
☻ The above sphenoid ridge that articulates with the perpendicular plate of the sphenoid.
And on each side:
☻ A surface where the hole in the sphenoid sinus.
☻ A anfractuous semiceldillas surface, which articulates with the lateral masses of the sphenoid.
BOTTOM SIDE
It is part of the bed of the nostrils; It presents:
☻ The lower sphenoid ridge, it articulates with the vomer and ends before the peak or rostrum.
☻ Two triangular surfaces or turbinates of berlin, limited by the vaginal process of the pterygoid process.
BACK SIDE
It is welded to the basilar process of the occipital.

LATERAL SIDES
present:
☻ The two roots of the lower wing and including the optical conduit.
☻ The larger wing root
☻ Among the roots of both wings, the groove tendon zinn (suboptico tuber).
☻ The channel cavernous sinus.
ALAS MINORS
Are two triangular sheets.
Born of the sphenoid body by two roots that define the body along with the optical conduit, through which the optic nerve and artery ophthalmia have two faces and two edges.
TOP FACE
Endocranial is part of the anterior floor of the skull base
BOTTOM SIDE
Exocraneal, it is part of the upper wall of the orbit.
EDGE PAST
It articulates with the horizontal segment of the front edge.
EDGE BACK
It is free and limits the superior orbital fissure.
VÉRTICES
It has three vertices:
☻ anterolateral: the processes is ensiforme
☻ Posterior constitutes prior clinoid process.
☻ Internal: is the roots, the body adheres.
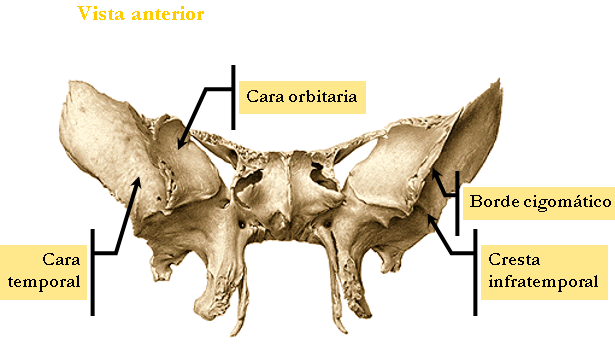
MORE WINGS
There are two flat sheets that emerge from the faces of the sphenoid body, have two faces and two edges.
Ad
endocranial FACE☻ The endocraneal face is concave, is part of the middle floor of the skull base has three holes and two unconscious constant.
☻ The largest round hole, it gives way to the maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve.
☻ The foramen ovale, it gives way to inner rema maxillary nerve and trigeminal meningeal artery minor branch of the internal maxillary.
☻ The smaller round hole, it gives way to the middle meningeal artery branch of the internal maxillary and meningeal branch of mandibular nerve.
☻ The hole Vesalius, inconstant gives way to an emissary vein.
☻ The top hole of the innominate duct Arnold, inconstant, which gives way to the deep petrosal nerves lower and the lower surface petroso.
exocraneal FACE
☻ is divided into two parts by the malar ridge.
☻ The malar crest articulates with the orbital process of the malar.
☻ The orbital surface forms part of the outer face of the orbit.
☻ The temporocigomatica face, divided by the esfenotemporal crest into two parts:
☻ In the upper or temporary part where the temporal muscle is inserted.
☻ The lower or subtemporal party filing the sphenoid tubercle, which gives insertion to the temporal and lateral pterygoid muscles.
INNER EDGE
It has three segments:
☻ The anterior segment, limits the superior orbital fissure.
☻ The superior orbital fissure leads to nerve, oculomotor (III par), ophthalmic, pathetic (IV pair) or its terminal branches and ophthalmia vein.
☻ The middle segment joins the body bone.
☻ The posterior segment is articulated with the front edge of the cliff, presents the semicanal of bone through the eustachian tube.
OUTER EDGE
It articulates with the temporal squama.
ANGLES
☻ The previous angle shows the front surface, which articulates with the frontal and pariental.
☻ The rear angle enters the space between the scale and the petrous and presents the sphenoid spine.
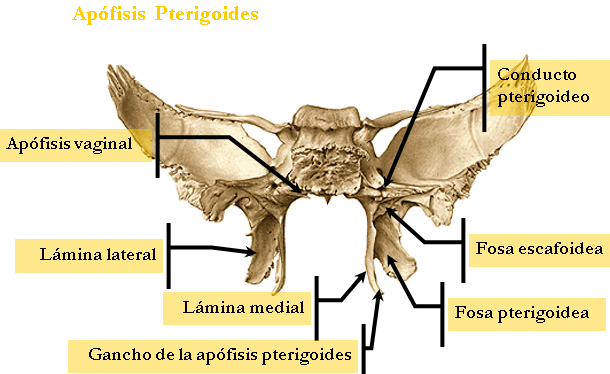
Pterygoid.
Implementation has a base and two wings:
BASE
It is implanted in the sphenoid by:
☻ The inner root underside of the body.
☻ External greater wing root.
☻ The two roots, with the body limit the vidiano duct, which leads to the vessels and nerve vadianos.
ALAS
☻ The two wings connected by its rear edge, forming among them the pit pterigoidea
☻ Beneath the two wings are separated by limiting the pterygoid recess, which corresponds to the pyramidal process of palatine.
☻ Vista as a whole has four faces:
EXTERNAL FACE
Forms the inner wall of the pit pterigomaxilar and gives attachment to the external pterygoid muscle.
INTERNAL FACE
It articulates forward with the Palladian, it follows the vaginal processes, along with the vomer esfenovomeriano limits lateral canal and presented along with the sphenoid process of the palatine limits the pterygopalatine driver.
FORMER FACE
Forms the rear wall of pit pterigomaxilar background of the previous hole presents vidiano duct.
BACK SIDE
It is part of the pterygoid fossa presents:
☻ The scaphoid fossa where the external perieslafilino muscle is inserted.
☻ In its external veli palatini inner wall is also inserted.
☻ In its outer wall the pterygoid interno.Esta face is limited by the rear edges of the two wings.
☻ The trailing edge of the inner wing presents: the recess for the fallopian Eustaquioy a hook where the external perieslafilino muscle is reflected.
☻ The trailing edge of the outer wing has civini Thorn. For pterygospinous ligament.
☻ The sphenoid gives attachment to 22 muscles on each side.
☻ In older muscles: Temporal, external pterygoid.
☻ In the lesser wings muscles: external oblique, upper eyelid lift and through the ring of Zinn to the four right eye.
☻ In the pterygoid muscle: medial pterygoid, the external pterygoid, the external perieslafilino and superior pharyngeal constrictor
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario