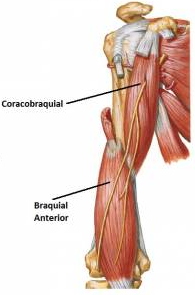
MAJOR MUSCLE CHEST
SHORT DESCRIPTION
- Dorsi, flattened and triangular.
- Thin medially and laterally thick.
- It is separated from the deltoid muscle, forming the groove deltopectoral.
OCUPA
- Located on the front and upper chest.
- In front of the pectoralis minor.
- It extends from the chest to the humerus.
ORIGIN: Portion:
- Clavicular: 2/3 medial aspect of the anterior border of the clavicle. (Descending fibers)
- Sternal: corresponding half of the sternum, 5-6 first costal cartilages. 4 and 5 are most important.
- Abdominal: Front of the sheath of the rectus abdominis.
INSERTION
intertubercular anterior lip of the groove, using 2 fascicles:
- Previous: Continuation of clavicular and sternal top of the fibers.
- Rear: Formed by the other parts of the muscle.
These two issues are joined by means of a fascicle.
INNERVATION : Nerves of the pectoralis major and minor, Brachial Plexus.
FUNCTION
- Adductor and medial rotator arm.
- fixed in the humeral point, raises the thorax. (Raising the whole body).