SITUATION
CONFIGURATION
It has four parts, Which in relation to the foramen magnum are: Previous or basilar Processes, the lateral masses; and posterior occipital scale.
BODY OR processes BASILAR
Quadrilateral shape, has two faces and four edges.
Exocraneal.- Face Presents:
- Online media pharyngeal tubercle, the navicular fossa pharyngeal With fossa.
- On each side; concavity previous two curves: Back or muscle rectus muscle insertion That has lower neck.
- The above or sinostosica, ahead of Which the largest rectus inserted neck.
endocraneal face
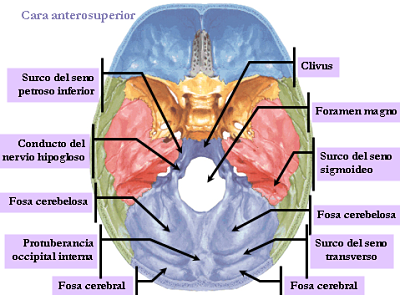
It presents clivus in relation to the pons and the medulla oblongata.
side edges
These edges are joined by a temporary fibrocartilage.
Leading edge
It is welded to the rear face of the sphenoid body.
rear edge
Forward boundary of the foramen magnum and lateral sides continuous With the masses.
lateral masses
It has two faces, two edges and two extremities.
Exocraneal face .- Presents:
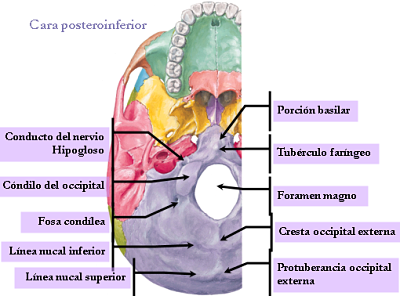
- The occipital condyle, elongated forward and inward, narrowed in the middle.
- The anterior condylar fossa anterior condylar Where the conduit passes through the hypoglossal nerve Which (XII pair) opens.
- The posterior condylar fossa posterior condylar Which opens the hole is inconstant.
- An area of the jugular veneer for insertion of the lateral rectus muscle.
Endocranial face .- Presents:
- The occipital tuber.
- The previous internal condylar canal orifice.
- The jugular sinus segment lateral channel.
inner edge
Laterally limits the foramen magnum.
outer edge
It articulates With the jugular facet of the storm, limiting the hole torn posterior and features:
The jugular spine That divide it into two parts:
- The hole torn posterior is divided into two parts by the jugular thorns, temporal and occipital and the ligament That unites them.
- The front part is subdivided into two segments, above the crossed by the glossopharyngeal and inferior petrosal sinus, and later by the neumogastrico and cord.
- The back is crossed by the origin of the internal jugular.
forelimb
It Continues With the basilar process.
hindlimb
It Continues With the scale.
occipital squama
Diamond-shaped, it has two faces and four edges.
exocraneal face
.- Presents:
- The external occipital protuberances or inion.
- The external occipital crest.
- The occipital upper and inner lines or nuchal Among Which are inserted:
- Towards the middle of the rear trapeze muscles, more complex, less straight.
- Towards the occipital part lateral muscles, sternocleidomastoid, splenius, and more posterior oblique lower rectum.
Endrocraneal face .- presents:
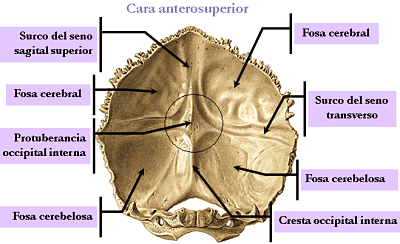
- The occipital internal protuberances excavates for subsequent venous confluent.
- The channel of the superior sagittal sinus.
- The channels of the lateral sinuses.
- The internal occipital crest, Gives to the insertion mouth of the cerebellum.
- The four occipital pits separated by the above formations.
upper edges
They articulate With lambdoid suture forming the parietal, Whose top angle is called lambda. Bottom Edges
Articulate With the scale of the storm, at the bottom are continuous With the lateral masses and finally the lower angle of the scale limits the foramen magnum.
The insertion Gives occipital muscles to twelve:
- In the occipitofrontal flake muscles, trapezius, sternocleidomastoid, splenius, more complex, lower back straight, straight posterior oblique larger and smaller are inserted. - In the jugular Processes the lateral rectus muscle.
- In the basilar Processes, muscles: lower rectum, anterior rectus, and the constrictor of the larynx.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario