CHARACTERISTICS
The skull has the following characteristics:
☻ ovoid shape with thick posterior limb.
☻ Capacity 1400-1500 cc.
CONFIGURATION
The skull is divided into vault and base, whose limit is marked by a line passing through the nasofrontal groove, orbital arches, the superior curved line of the occipital, and the internal occipital protuberance.
It can describe an outer surface and a bottom.
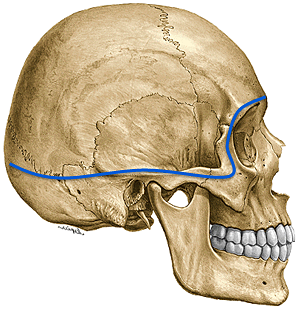

EXTERNAL or exterior SKULL
VAULT
Convex presents:
In the midline; glabella, the metopic, the sagittal suture, the Obelion, the parietal holes and internal occipital eminence.
To the sides; the frontal parietal eminence, the coronal suture, the parietal eminence and lambdoid suture.
Below the parietal eminence is temporary, limited pit:
☻ Above, the superior temporal curved line; the lateral frontal crest and the external orbital process thereof.
☻ Down by the zygomatic arch.
☻ Forward on the posterior edge of the malar bone.
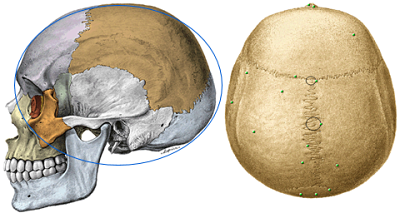 BASE
BASE

It is divided into two parts.
FACIAL PORTION
Integrated by the ethmoid, the frontal portion orbitonasal and sphenoid presents:
☻ The ethmoid recess, nasal spine and orbital frontal passages.
☻ The underside of the ethmoid.
☻ The above and lower face of the sphenoid, the underside of the wings and exocraneal lower face of the sphenoid, and the largest, oval and round menor.Las pterygoid round holes.
SERVING temporooccipital
presents:
In the midline, the occipital basilar processes, the foramen magnum and the external occipital crest.
Laterally it can be divided into two triangles by a line from the internal wing of the pterygoid to the posterior edge of the mastoid.
The anterolateral triangle presents:
☻ The underside of the temporal with: the temporal condyle, glenoid cavity, mastoid process, the digastric groove, the yuxtamastoidea eminence, carotid hole, the jugular fossa, the styloid process, the fixing hole through bone ka tube.
☻ The rear end of the wing of the sphenoid.
The posteromedial triangle presents:
☻ The lateral mass of the occipital condyle and the pits and anterior and posterior condylar conductive.
☻ The scale of the occipital with occipital upper and lower curves.


INTERNAL CONFIGURATION SKULL
VAULT
concave; It presented in the midline: the channel of the superior sagittal sinus, the pits of Pacchioni.
On the sides, the front pit, parietal pit, and channels for the middle meningeal.
It has three regions or floors.
FORMER FLAT ETMOIDOFRONTAL
The vertical portion extends from the front to the pituitary tubercle and the posterior edge of the lesser wings of the sphenoid, presents:
☻ The blind hole, crista galli processes olfactory channels and the cribriform lamina; orbital eminence formed by the front and the lesser wings of the sphenoid.
☻ The sphenoid jugum, the optical channel and the hole of the optical conduit.
MIDDLE FLOOR esfenotemporal
It ranges from the pituitary tubercle and trailing edge of the lesser wings of the sphenoid to the quadrilateral plate and the upper edge of the cliff, presents:
☻ The pituitary fossa, the anterior and posterior clinoid process.
☻ Cavernous channels.
☻ The esfenotemporales graves where the biggest round holes, oval, teres minor, Vesalius, lacerum and Arnold, the fosita Gasser ganglion, the hialo tubes and the arcuate eminence.
FLAT BACK AND occipitotemporal
It ranges from the quadrilateral plate and upper edge of the cliff to the canal lateral sinus and internal occipital protuberances, presents:
☻ The inner hole of the inner ear canal, the pit subarcuata, the opening of the aqueduct lobby.
☻ condylar ducts, the hole torn posterior.
☻ The cerebral and cerebellar occipital cavity, the channel lateral sinus in three portions.
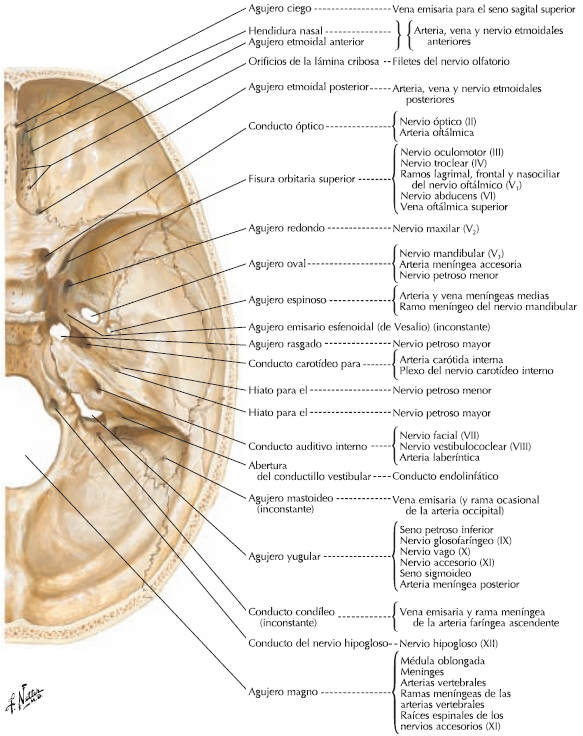
Ruviere A. H. Delmas Human Anatomy Descriptive, topographic and functional. 11th Edition . Editorial MASSON, SA 2005 pages 83-90
☻ The cerebral and cerebellar occipital cavity, the channel lateral sinus in three portions.

Ad
BIBLIOGRÁFICARuviere A. H. Delmas Human Anatomy Descriptive, topographic and functional. 11th Edition . Editorial MASSON, SA 2005 pages 83-90

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario