The temporal bone couple , is located on the side and bottom of the skull, sphenoid outside, front and outside the occipital parietal below.
CONFIGURATION
- The time comes from three primitive portions, the timpanal bone, rock and flake, which differ to lots of classical description.
- The bones can be recognized by the rest of the sutures that unite.
- The corresponding parts to these bones that do not fit the classic description will be given at the bottom of page.

Squamous portion O FLAKE
It has two faces and a circumferential edge.
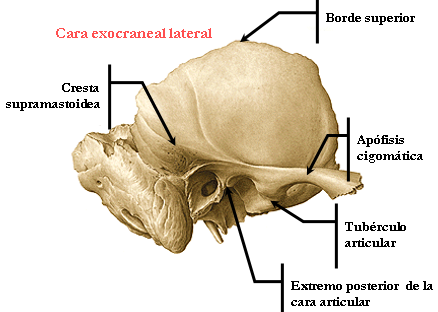
Exocraneal FACE.
It is divided by the zygomatic process into two pairs.
Zygomatic processes.
They have two segments:
The basal segment, on its upper face a channel for the temporalis muscle.
- Its underside has the two roots of the zygomatic process.
- The longitudinal root is directed backwards, presents the posterior zygomatic tubercle and then take the name of supramastoidea crest.
- The cross is the root of the temporal condyle and presented in conjunction with the above the previous zygomatic tubercle.
The anterior segment or zygomatic process itself that is free.
It has a front side and back side.
A top for insertion of the temporal fascia and a lower edge for insertion of the masseter muscle edge.
TOP OF FLAKE
It is smooth and convex, which inserts the temporalis muscle. It has channels for the branches of the posterior deep temporal artery.
BOTTOM FLAKE BASILAR
presents:
- The condyle temporary or transverse root of the zygomatic process.
- The glenoid, divided by the sulcus Glasser in a joint front and rear unarticulated
- The tubers anterior and posterior zygomatic
- The subtemporal surface bed of the zygomatic nostril.
endocranial FACE
It is in relation to brain sulci and has channels for the middle meningeal artery.
circumferential edge
It comprises two parts:
- The sticky part is confused with the mastoid portion and is indicated by the petroescamosa and Glasser limpanoescamosa or fissures.
- The free part begins in the angle between the scale and the rock and ends in the parietal notch separating the scale of the mastoid, it articulates with the parietal and the wing of the sphenoid.
SERVING mastoid
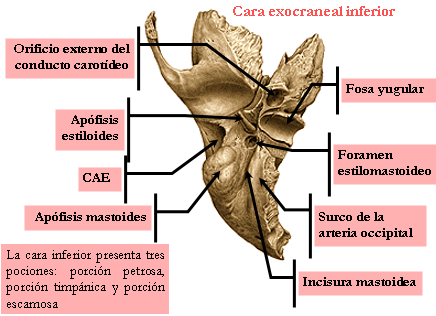
Located behind and below the ear canal has two faces and a circumferential edge.
exocraneal FACE
presents:
- The remains of the petroescamosa fissure.
- Above the spine and vascular suprameatal holes.
Under.
- Roughness for insertion of the occipital muscles, splenius and sternocleidomastoid.
The external orifice of the mastoid canal, crossed by an emissary vein.
Mastoid having two separated by a front edge and a rear faces.
The outer face gives attachment to the sternocleidomastoid and less complex.
The inner face presents: the digastric groove for digastricus and a channel for the occipital artery, separated from the former by the eminence yuxtamastoidea.
Endocranial FACE.
- Onward it joins the petrous pyramid
- Backwards presents the channel of the descending portion of the lateral sinus and the internal bore of the mastoid canal
circumferential edge
They articulated the parietal and occipital.
The rock is shaped like quadrangular pyramid base, has four faces, four edges, a base and an apex.
Anterosuperior aspect.
Intracranial is presented:
- The arcuate eminence
- The hiatus hiatuses tubes and fittings where it runs the superficial and deep petrosal nerves.
- The fossa which houses the ganglion Glasser.
- The tegmen tympani tour of the superior sulcus petroescamosa.
Posterosuperior FACE.
Intracranial presents:
- The inlet to the inner ear canal, through which pass the facial nerve (VI pair), Wrisberg broker and auditory VIII pair).
- The pit subarcuata the previous hole the petromastoideo duct.
- The nail posterior fossa with the hole through the aqueduct lobby.
Anteroinferior FACE.
Extracranial presents:
- Vaginal process.
- Tubal timpanal process of the bone.
- The holes in the ducts and duct hammer bone of the Eustachian tube.
- A channel next to the esfenopetroso sphenoid or tubal channel corresponding to the fibrocartilaginous portion of the Eustachian tube.
FACE posterior.
Extracranial presents:
- The styloid process in which the bunch of Riolan is inserted.
- The Stylomastoid hole or bottom hole of the aqueduct of the facial nerve.
- The veneer jugular for the jugular process of the occipital.
- The jugular fossa for within the internal jugular vein with the introitus ositum for auricular branch of the vagus nerve (X par).
- The lower orifice of the carotid canal.
- The bottom hole of the tympanic canal that leads to the nerve branch of the glossopharyngeal Jacobson.
- A rough surface for insertion of the internal veli palatini.
TOP EDGE
It presents the superior petrosal sinus channel, a recess for the trigeminal nerve.
EDGE PAST
- Behind me is attached to the flake, ahead is separated from it by an incoming angle, and articulates with the sphenoid and limits the hole lacerum.
- The hole lacerum is crossed by the greater superficial petrosal nerve, deep petrosal minor, and the petro - occipital sinus.
BOTTOM EDGE
This filing at the lower edge of the vaginal process and tubal process.
EDGE BACK.
presents:
- The jugular veneer, by the occipital limiting the hole torn back, spine presents jugular by the homonymous occipital divides this into two parts:
- For the previous pass glossopharyngeal (IX) and spinal pair (XI pair).
- On the back passes the Gulf of the jugular vein.
In the posterior segment is the petrous pit where the aqueduct snail opens and the petrosal ganglion of glossopharyngeal staying.
Two channels, superior in relation to the inferior petrosal sinus and lower the petro-occipital sinus, separated by an area with which it articulates with the fibrocartilage that attaches it to the occiput.
BASE.
The base is confused with the mastoid, and is represented by the opening of the ear canal externo.El smooth contour of the top and bottom rough for insertion of fibrocartilage the ear canal ..

Truncated corresponds to the angle between the body and the greater wing of the sphenoid.
It presents the top hole of the carotid canal, and bound together with the sphenoid lacerum hole.
- Which is divided into two parts by the sphenoid lingula the outside is crossed by shallow and superficial greater petrosal nerves smaller, internal is in relation to the internal carotid artery.
- In the temporary 13 muscles are inserted without cutting the muscles of the inner ear.
- In the scale the temporalis muscle.
- In the occipital mastoid muscles, posterior auricular, sternocleidomastoid, splenius, less complex diagnosis.
- In the zygomatic processes the masseter muscle.
- In the styloid muscles: stylohyoid, estilogloso and Stylopharyngeus.
- In the crag, internal veli palatini and petrofaringero.

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario